Tomcat的请求处理流程分析
0 条评论Tomcat 请求处理流程
首先 在 org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11Processor#service 断点
访问http://localhost:8080/index.jsp
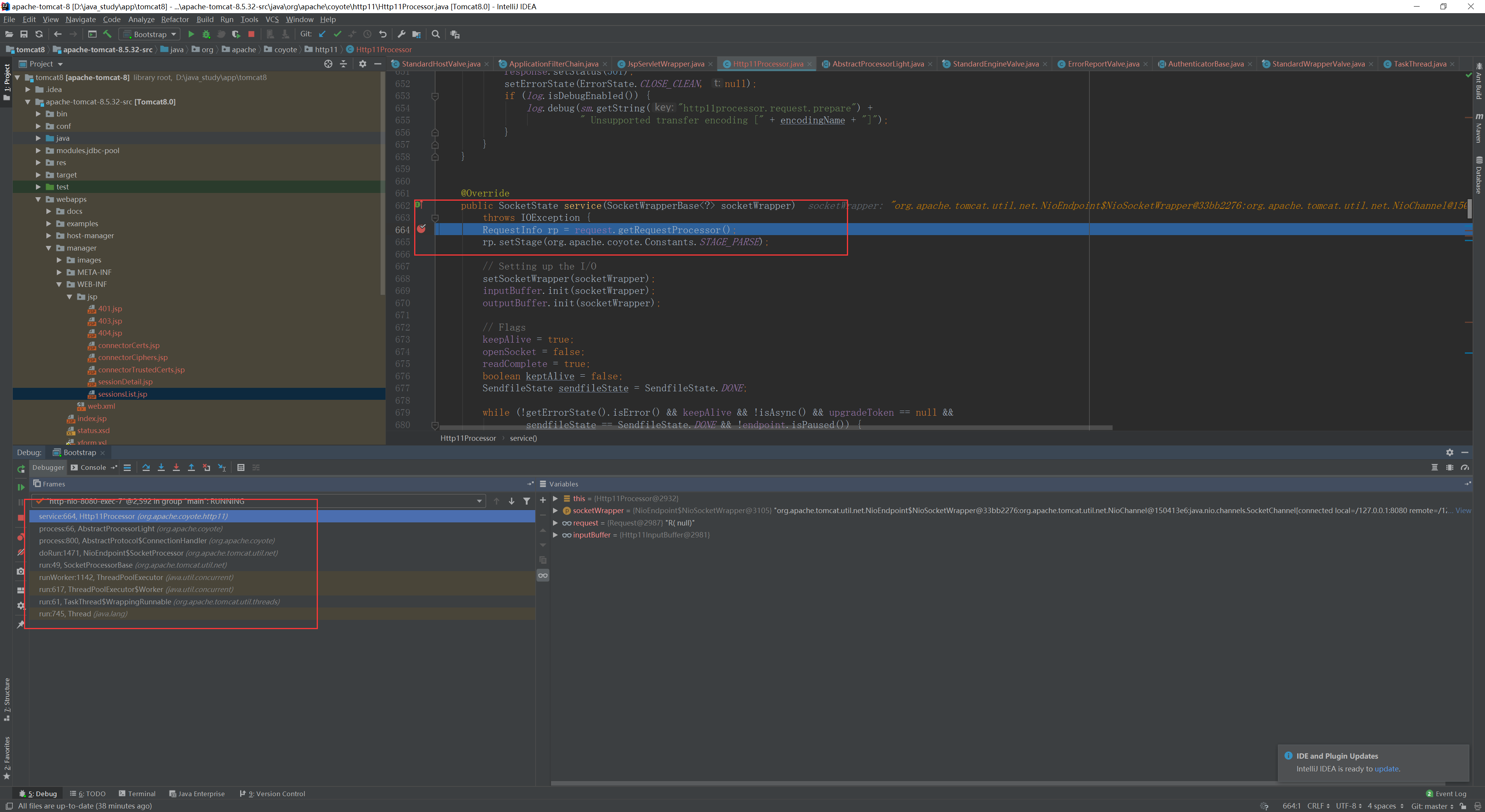
在java.lang.Override#run中
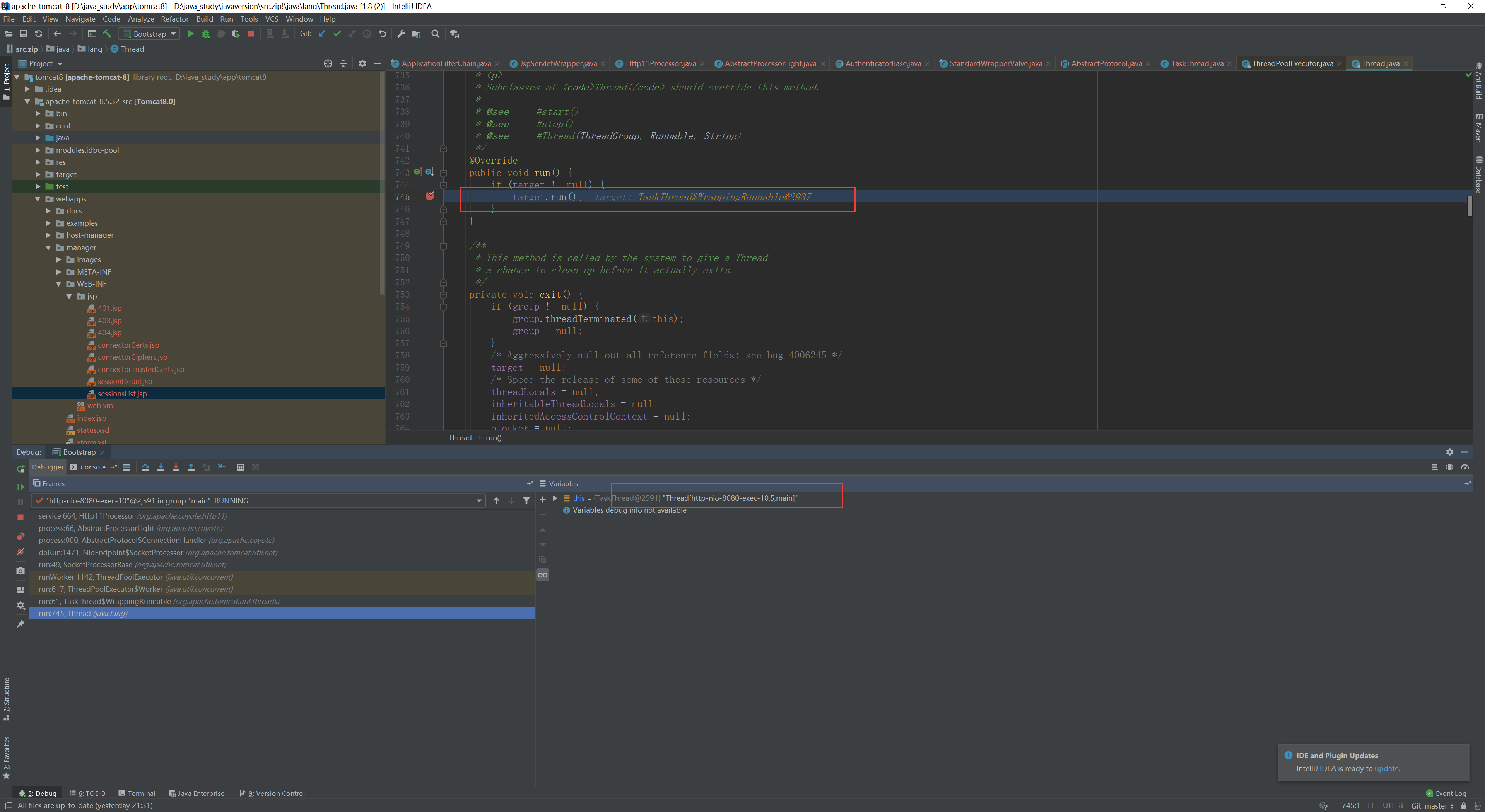
我们可以看到进入的的是一个http的线程
在tomcat启动时
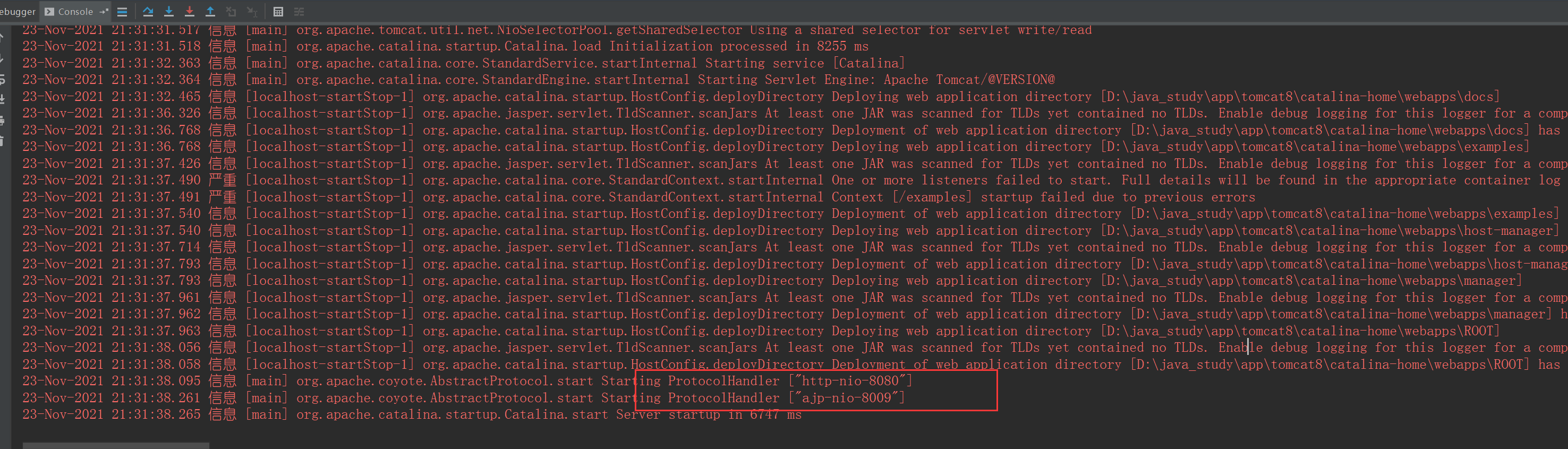
看出开启了两个线程,一个http,一个ajp,通过8080访问的是http协议。
org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11Processor#service 代码如下:
public SocketState service(SocketWrapperBase<?> socketWrapper)
throws IOException {
RequestInfo rp = request.getRequestProcessor();
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_PARSE);
// Setting up the I/O
setSocketWrapper(socketWrapper);
inputBuffer.init(socketWrapper);
outputBuffer.init(socketWrapper);
// Flags
keepAlive = true;
openSocket = false;
readComplete = true;
boolean keptAlive = false;
SendfileState sendfileState = SendfileState.DONE;
while (!getErrorState().isError() && keepAlive && !isAsync() && upgradeToken == null &&
sendfileState == SendfileState.DONE && !endpoint.isPaused()) {
// Parsing the request header
try {
if (!inputBuffer.parseRequestLine(keptAlive)) {
if (inputBuffer.getParsingRequestLinePhase() == -1) {
return SocketState.UPGRADING;
} else if (handleIncompleteRequestLineRead()) {
break;
}
}
if (endpoint.isPaused()) {
// 503 - Service unavailable
response.setStatus(503);
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, null);
} else {
keptAlive = true;
// Set this every time in case limit has been changed via JMX
request.getMimeHeaders().setLimit(endpoint.getMaxHeaderCount());
if (!inputBuffer.parseHeaders()) {
// We've read part of the request, don't recycle it
// instead associate it with the socket
openSocket = true;
readComplete = false;
break;
}
if (!disableUploadTimeout) {
socketWrapper.setReadTimeout(connectionUploadTimeout);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("http11processor.header.parse"), e);
}
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CONNECTION_NOW, e);
break;
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
UserDataHelper.Mode logMode = userDataHelper.getNextMode();
if (logMode != null) {
String message = sm.getString("http11processor.header.parse");
switch (logMode) {
case INFO_THEN_DEBUG:
message += sm.getString("http11processor.fallToDebug");
//$FALL-THROUGH$
case INFO:
log.info(message, t);
break;
case DEBUG:
log.debug(message, t);
}
}
// 400 - Bad Request
response.setStatus(400);
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, t);
getAdapter().log(request, response, 0);
}
// Has an upgrade been requested?
Enumeration<String> connectionValues = request.getMimeHeaders().values("Connection");
boolean foundUpgrade = false;
while (connectionValues.hasMoreElements() && !foundUpgrade) {
foundUpgrade = connectionValues.nextElement().toLowerCase(
Locale.ENGLISH).contains("upgrade");
}
if (foundUpgrade) {
// Check the protocol
String requestedProtocol = request.getHeader("Upgrade");
UpgradeProtocol upgradeProtocol = httpUpgradeProtocols.get(requestedProtocol);
if (upgradeProtocol != null) {
if (upgradeProtocol.accept(request)) {
// TODO Figure out how to handle request bodies at this
// point.
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_SWITCHING_PROTOCOLS);
response.setHeader("Connection", "Upgrade");
response.setHeader("Upgrade", requestedProtocol);
action(ActionCode.CLOSE, null);
getAdapter().log(request, response, 0);
InternalHttpUpgradeHandler upgradeHandler =
upgradeProtocol.getInternalUpgradeHandler(
getAdapter(), cloneRequest(request));
UpgradeToken upgradeToken = new UpgradeToken(upgradeHandler, null, null);
action(ActionCode.UPGRADE, upgradeToken);
return SocketState.UPGRADING;
}
}
}
if (!getErrorState().isError()) {
// Setting up filters, and parse some request headers
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_PREPARE);
try {
prepareRequest();
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("http11processor.request.prepare"), t);
}
// 500 - Internal Server Error
response.setStatus(500);
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, t);
getAdapter().log(request, response, 0);
}
}
if (maxKeepAliveRequests == 1) {
keepAlive = false;
} else if (maxKeepAliveRequests > 0 &&
socketWrapper.decrementKeepAlive() <= 0) {
keepAlive = false;
}
// Process the request in the adapter
if (!getErrorState().isError()) {
try {
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_SERVICE);
getAdapter().service(request, response);
// Handle when the response was committed before a serious
// error occurred. Throwing a ServletException should both
// set the status to 500 and set the errorException.
// If we fail here, then the response is likely already
// committed, so we can't try and set headers.
if(keepAlive && !getErrorState().isError() && !isAsync() &&
statusDropsConnection(response.getStatus())) {
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, null);
}
} catch (InterruptedIOException e) {
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CONNECTION_NOW, e);
} catch (HeadersTooLargeException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("http11processor.request.process"), e);
// The response should not have been committed but check it
// anyway to be safe
if (response.isCommitted()) {
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_NOW, e);
} else {
response.reset();
response.setStatus(500);
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, e);
response.setHeader("Connection", "close"); // TODO: Remove
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
log.error(sm.getString("http11processor.request.process"), t);
// 500 - Internal Server Error
response.setStatus(500);
setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, t);
getAdapter().log(request, response, 0);
}
}
// Finish the handling of the request
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDINPUT);
if (!isAsync()) {
// If this is an async request then the request ends when it has
// been completed. The AsyncContext is responsible for calling
// endRequest() in that case.
endRequest();
}
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDOUTPUT);
// If there was an error, make sure the request is counted as
// and error, and update the statistics counter
if (getErrorState().isError()) {
response.setStatus(500);
}
if (!isAsync() || getErrorState().isError()) {
request.updateCounters();
if (getErrorState().isIoAllowed()) {
inputBuffer.nextRequest();
outputBuffer.nextRequest();
}
}
if (!disableUploadTimeout) {
int soTimeout = endpoint.getConnectionTimeout();
if(soTimeout > 0) {
socketWrapper.setReadTimeout(soTimeout);
} else {
socketWrapper.setReadTimeout(0);
}
}
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_KEEPALIVE);
sendfileState = processSendfile(socketWrapper);
}
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDED);
if (getErrorState().isError() || endpoint.isPaused()) {
return SocketState.CLOSED;
} else if (isAsync()) {
return SocketState.LONG;
} else if (isUpgrade()) {
return SocketState.UPGRADING;
} else {
if (sendfileState == SendfileState.PENDING) {
return SocketState.SENDFILE;
} else {
if (openSocket) {
if (readComplete) {
return SocketState.OPEN;
} else {
return SocketState.LONG;
}
} else {
return SocketState.CLOSED;
}
}
}
}
在这里面
tomcat先对io进行初始化,包括输入输出,对http做了一些处理,包括各类请求头,比如Connection、Upgrade,来实现http请求头的一些作用。
然后调用prepareRequest()方法
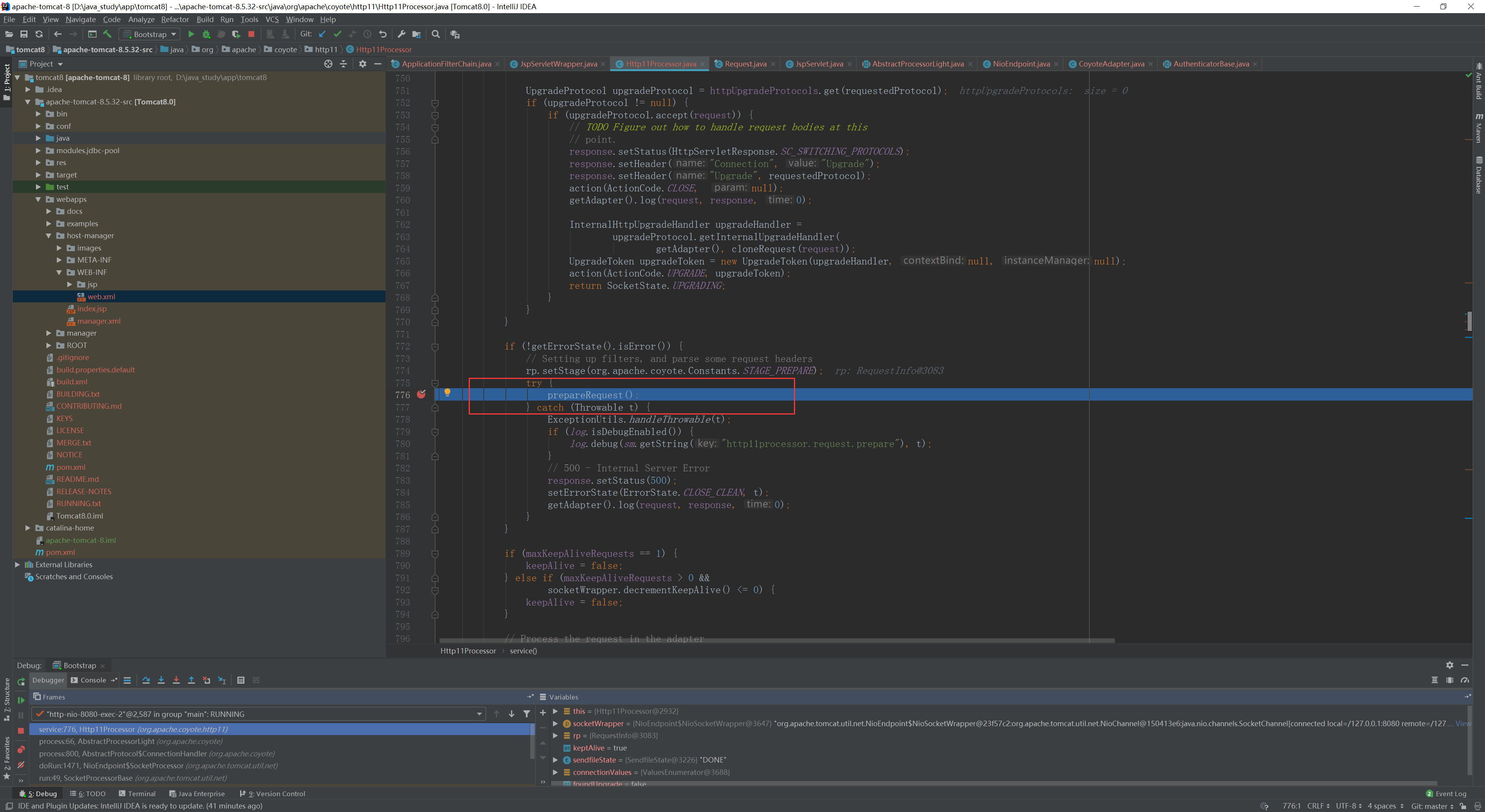
在此方法里面就是对我们熟悉的 request 类进行处理
完成协议等初始化后,就开始调用service了
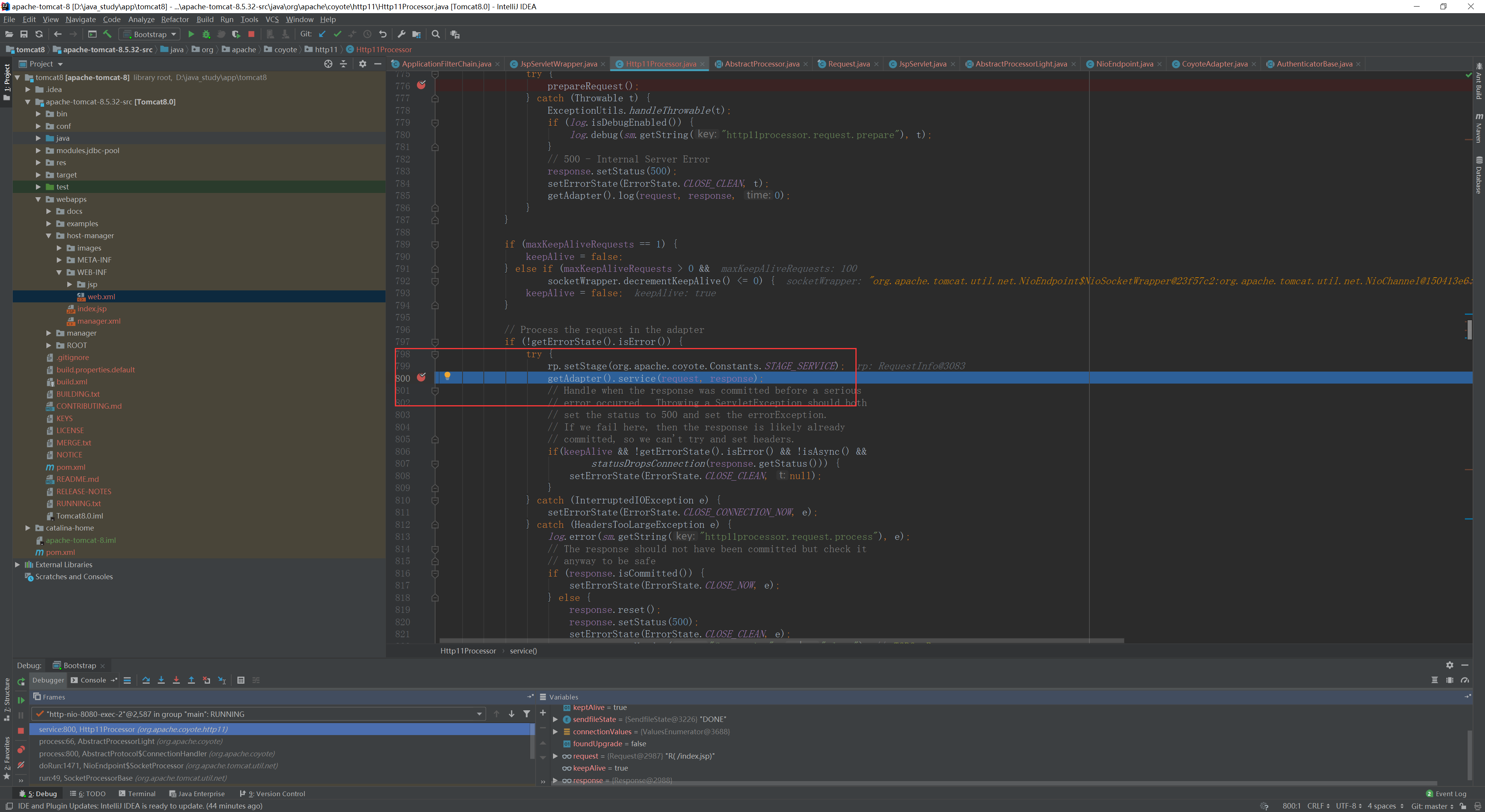
然后就进入了一层层的invoke,调用栈如下:
invoke:199, StandardWrapperValve (org.apache.catalina.core)
invoke:96, StandardContextValve (org.apache.catalina.core)
invoke:493, AuthenticatorBase (org.apache.catalina.authenticator)
invoke:140, StandardHostValve (org.apache.catalina.core)
invoke:81, ErrorReportValve (org.apache.catalina.valves)
invoke:650, AbstractAccessLogValve (org.apache.catalina.valves)
invoke:87, StandardEngineValve (org.apache.catalina.core)
在org.apache.catalina.core.StandardHostValve#invoke中
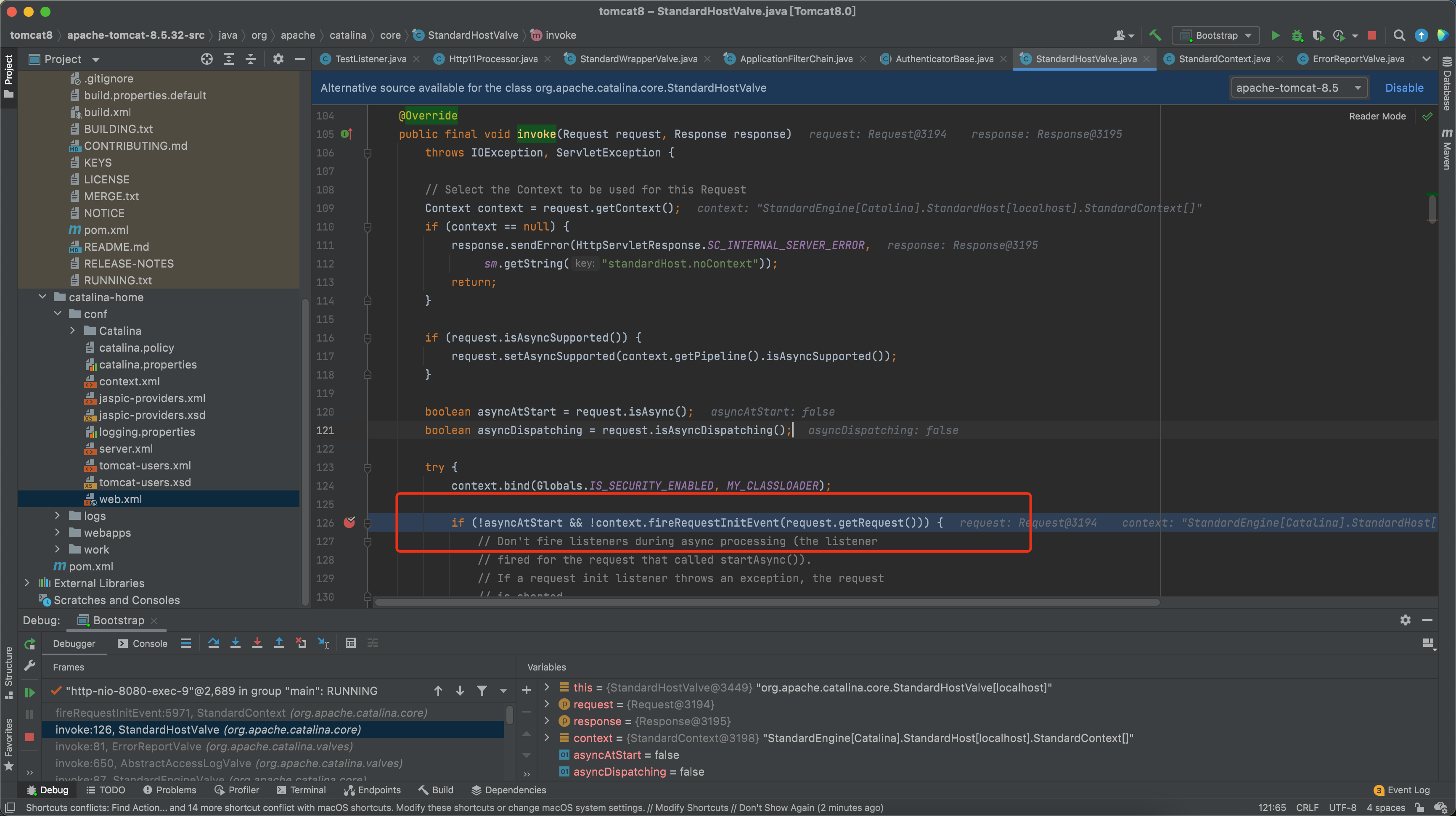
跟进org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext#fireRequestInitEvent
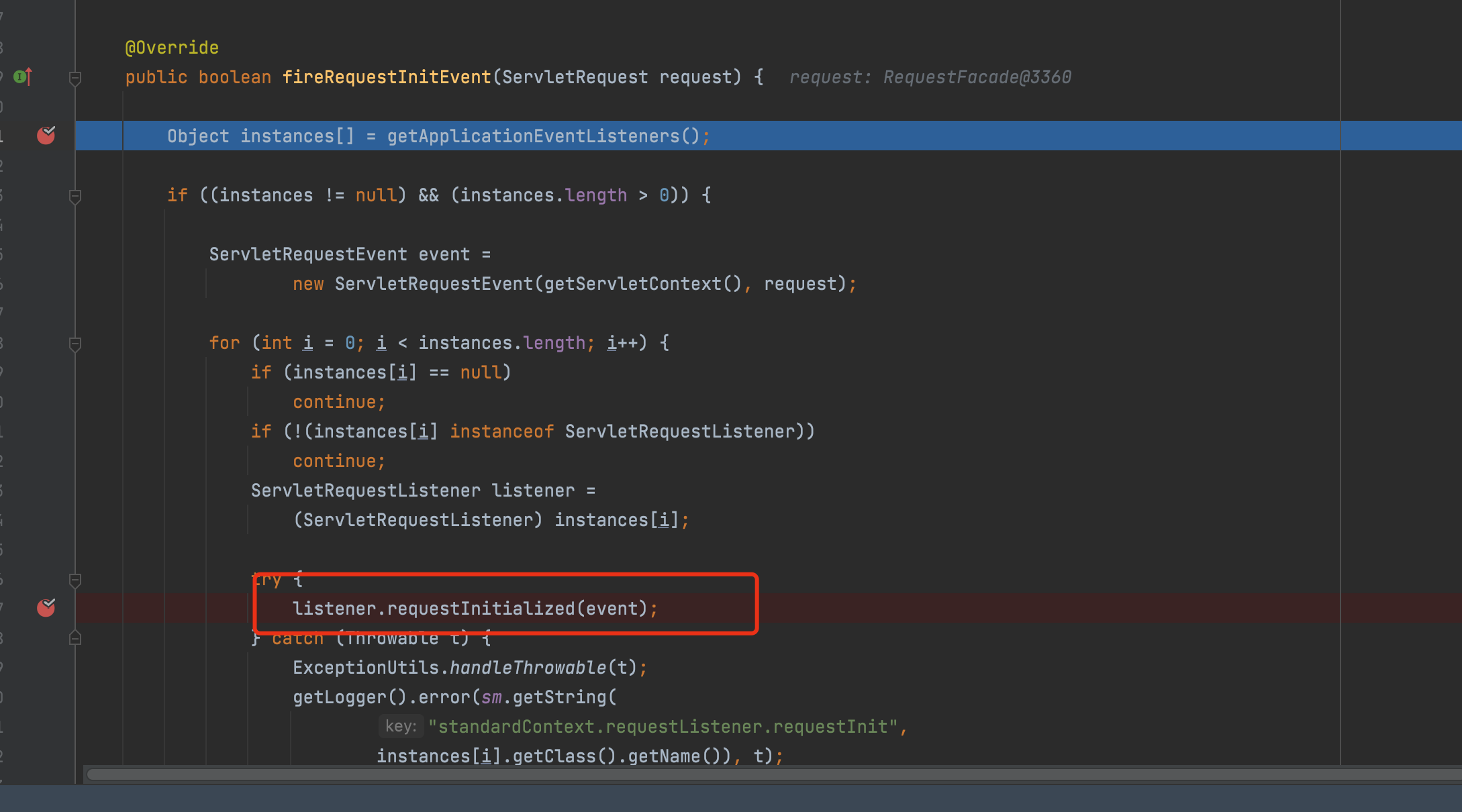 循环调用了所有listener的requestInitialized方法。
循环调用了所有listener的requestInitialized方法。
listener.requestInitialized(event);
最后进入
org.apache.catalina.core.StandardWrapperValve#invoke
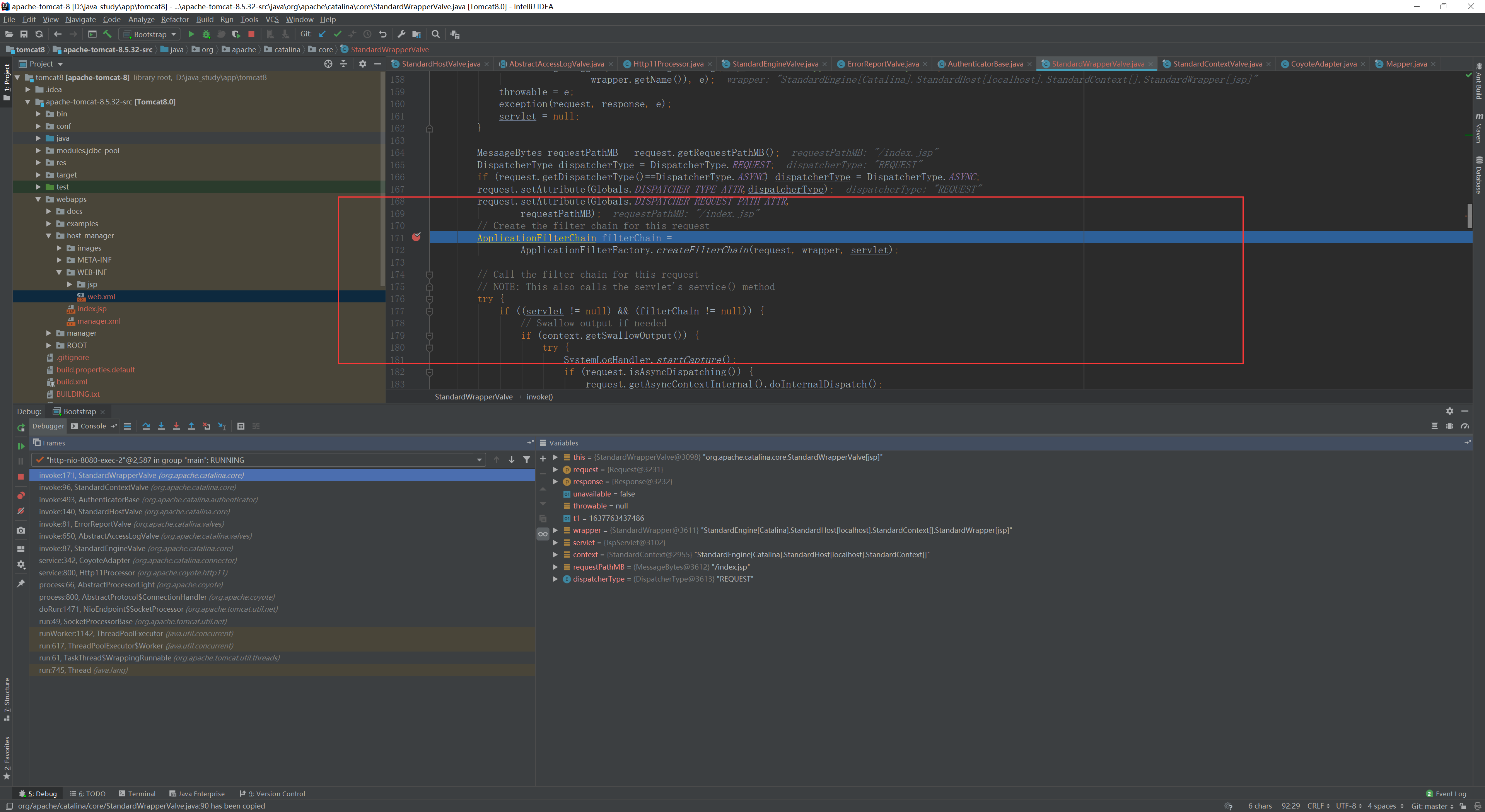
这里我们看到了filterChain 即一个过滤链,平时做的过滤也在这里
然后便进入了
org.apache.catalina/.core.ApplicationFilterChain.java#doFilter
再进入internalDoFilter
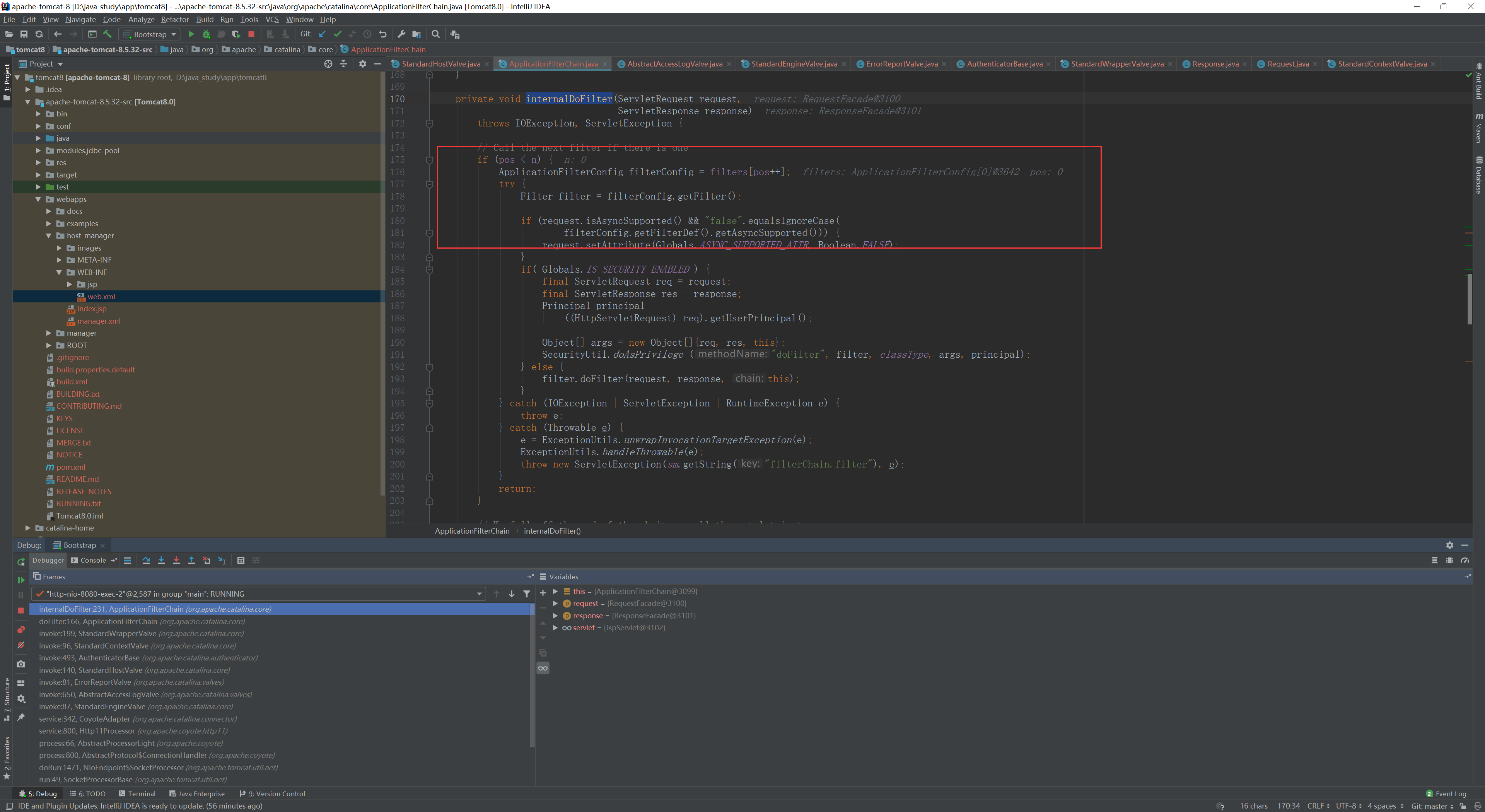
这里我们可以看到是一个for循环来处理多个filter,默认安装下没有fileter所以直接过去了
到了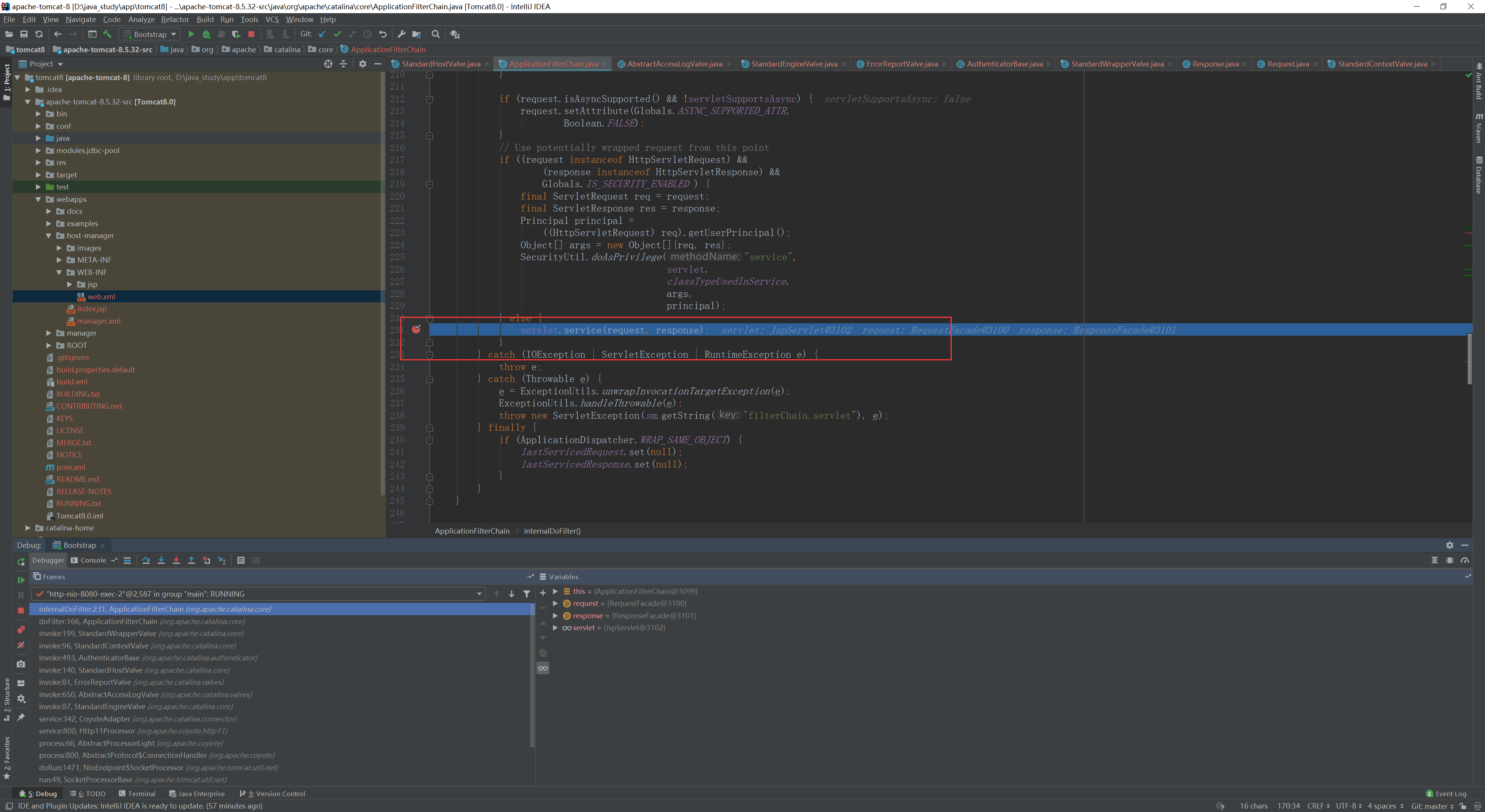
servlet.service(request, response);
跟进
进入了
org.apache.jasper.servlet.JspServlet.java#service
进入这里基本上就到了调服务阶段了
我们看看JspServlet在哪设置的
在conf/web.xml中我们看到下面的配置
<servlet>
<servlet-name>jsp</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.apache.jasper.servlet.JspServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>fork</param-name>
<param-value>false</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>xpoweredBy</param-name>
<param-value>false</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>3</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>jsp</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.jsp</url-pattern>
<url-pattern>*.jspx</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
看的出来系统配置了url访问为.jsp的地址便调用org.apache.jasper.servlet.JspServlet,在以tomcat搭建的系统中,我们便可以以此作为审计的入口

